Introduction
Rheumatoid factor (RF) is one of the oldest laboratory markers widely used in rheumatology. It is an antibody (most often of the immunoglobulin M [IgM] class, less frequently of the immunoglobulin A [IgA] and immunoglobulin G [IgG] classes) directed against the Fc fragment of immunoglobulin G. Rheumatoid factor production is considered to be a part of the normal immune response to antigenic stimulation. The main functions of RF are as follows [1]:
accelerating the clearance of immune complexes by increasing their size and facilitating their uptake by phagocytes;
participating in antigen presentation: membrane-associated RF molecules on the surface of B-lymphocytes facilitate the capture of immune complexes, their processing and presentation of antigens to T-lymphocytes.
Rheumatoid factor is most frequently detected in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS), cryoglobulinemia, mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD), some infectious and oncological diseases [2]. In systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), serological tests for RF are positive in about 25% of patients [3]. However, the association of RF with clinical manifestations, laboratory parameters, and its prognostic significance in SLE has not been sufficiently studied.
Previous studies have found a protective role of RF against the development of lupus nephritis [4–7] and an association with a higher incidence of malar rash, positivity for antibodies to Smith antigen, and hypothyroidism [5]. It has also been established that the level of IgA class RF is associated with an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), leukopenia, and positivity for antibodies to Ro/SSA and La/SSB antigens [4], while IgG class RF is associated with a lower incidence of serositis and hematologic disorders [8].
One study showed that positivity for RF of all three classes is associated with a lower level of IgG antibodies to cardiolipin (testing for antibodies to β2-glycoprotein was not routinely performed at the time of the study), and IgG class RF is also associated with a lower incidence of antiphospholipid syndrome [8]. A later study revealed a significantly lower number of patients positive for at least one of the antiphospholipid antibodies (APLA) among those who had a positive test for RF [3].
Despite the fact that RF is serological a marker of RA, its association with the frequency or severity of articular manifestations of SLE has not been established [3, 5, 9]. On the contrary, there is evidence of a protective role of IgG class RF against the development of arthritis in SLE [6]. Regarding disease activity, only one study has shown an association of IgM class RF levels with SLE activity [6].
The aim of the study was to investigate the associations between the presence and level of RF in the blood serum and the clinical and laboratory characteristics of patients with SLE.
Material and methods
In this retrospective tricentric cross-sectional study, we analyzed the medical records of 495 patients with SLE. These patients were under the outpatient and inpatient supervision of the staff of the Department of Internal Medicine No. 3 of the Bogomolets National Medical University at two rheumatological clinics (Alexander Clinical Hospital and Kyiv City Clinical Hospital No. 3) from 1994 to 2023 and the staff of the State Institution National Scientific Center Institute of Cardiology, Clinical and Regenerative Medicine named after Academician M.D. Strazhesko of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine from 2011 to 2023. Medical data were analyzed at the time of the initial visit of patients to these medical institutions. The diagnosis of SLE was established according to the classification criteria relevant at the time of the patient’s examination: ACR (American College of Rheumatology) (1982, updated in 1997) [10, 11], SLICC (Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics) (2012) [12], ACR/EULAR (American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology) (2019) [13]. The test for serum concentration of RF (without determining the immunoglobulin class) was performed in 206 patients (41.6%).
In each of these 206 patients, clinical manifestations of the disease and laboratory parameters were evaluated, if available in the medical records. For all patients, disease activity was assessed using the SLEDAI-2K scale [14], and the SLICC/ACR damage index (DI) [15] was determined at the time of the blood test for RF. Clinical manifestations were registered by a rheumatologist and/or by other doctors consulting, using diagnostic techniques if needed. In particular, in the case of a challenging skin rash a dermatologist was involved, as well as a neurologist, cardiologist and pulmonologist when nervous system, cardiovascular system or lung involvement was suspected. Schirmer’s test and the saliva production test were performed to confirm the diagnosis of sicca syndrome. Bone mineral density was evaluated by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Aseptic necrosis of bone was confirmed by MRI in all cases. Raynaud’s syndrome was diagnosed by personal doctor’s observation followed by capillaroscopy. Fever was defined as a body temperature ≥ 38.3°C in the armpit for more than 3 weeks in the last 3 months which could not be explained by other causes, including infections. Lupus nephritis was diagnosed by renal biopsy and/or according to renal SLEDAI-2K criteria [16] in the absence of other alternative causes. All pathology reports of patients who underwent kidney biopsy were reviewed to identify the ISN/RPS histological class of lupus nephritis [17]. The presence of renal involvement due to renal SLEDAI-2K criteria (score 4–16) was defined by presence of at least one subcomponent of the following on urinalysis: hematuria (> 5 RBC/HPF), proteinuria (> 0.5 g/24 hours), pyuria (> 5 WBC/HPF), urinary casts (heme-granular or red cell). Every patient was evaluated by a nephrologist for confirmation of renal involvement. Lymphadenopathy was confirmed in cases of lymph node enlargement in more than one region, which lasted for more than 3 weeks and had no other established cause. To exclude other causes, hematological and instrumental examinations were performed, including ultrasound diagnostic and/or computed tomography, and, if necessary, a hematologist consultation was conducted. Splenomegaly and serositis were confirmed by ultrasound investigation. Weight loss was considered significant if it exceeded 5% of body weight in 6 months or less. Other causes, e.g. hyperthyroidism or depression, were excluded.
The following methods were used for testing laboratory parameters:
antinuclear antibodies – indirect immunofluorescence test;
antibodies to double-stranded DNA, Smith antigen, chromatin, ribonucleoprotein, ribosomal P protein, centromere, Scl-70, Jo-1, Ro/SSA and La/SSB, antibodies to cardiolipin, β2-glycoprotein – enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA);
lupus anticoagulant – coagulation test;
RF, C-reactive protein (CRP), complement components C3 and C4 – turbidimetry technique;
antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide (ACPA) – chemiluminescent immunoassay technique;
creatinine level, serum protein level, daily proteinuria – colorimetric technique (glomerular filtration rate was calculated according to CKD-EPI formula);
complete blood count and urinalysis were performed by automated analyzers and manually if needed;
ESR was measured by the Westergren method.
Absolute values (n) and frequencies (%) were calculated to represent qualitative data. Quantitative parameters were presented as mean values with standard deviation (M ±SD) for normally distributed values or as the median and the first and third quartiles (Me [QI–QIII]) for non-normally distributed values. To assess the significance of the difference in mean and median values between the study groups, the parametric Student’s t-test and the nonparametric Mann-Whitney test were used, respectively. The χ2 criterion was applied to determine the consistency or difference in the distribution of parameters (frequency of detection) between the studied groups. Spearman’s rank correlation and Pearson’s linear correlation were used to establish the strength of interconnection between the parameters of the two samples. The difference between the groups was considered significant when the value of p < 0.05 was reached. To predict the binary initial feature by the influence of factor variables, the univariate logistic regression analysis was used. Statistical analysis was conducted using IBM SPSS Statistics Base v.22 for Windows, EZR version 1.61.
Bioethical standards
The approval of the Ethics Committee was obtained at the Bogomolets National Medical University (protocol No. 127, dated 02.12.2019), and at the State Institution National Scientific Center Institute of Cardiology, Clinical and Regenerative Medicine named after Academician M.D. Strazhesko of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine (protocol No. 13, dated 22.06.2020). The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Results
Among the patients included in the study, there were 173 women (84%) and 33 men (16%). The average age at the time of testing for the serum level of RF was 35 years (28–47 years), and the average disease duration was 48 years (15–120 months). The level of RF was higher than the reference value (> 12 U/ml) in 57 patients (27.7%). Among them, 10 patients (17.5%) were diagnosed with RA at the onset of the disease. Twenty-three patients with joint involvement (11.2%) were tested for the level of ACCP; only 2 (8.7%) of them were positive.
When comparing the groups of patients with presence and absence of RF in serum according to the main demographic, clinical and laboratory parameters (Table I), the following patterns were revealed:
Table I
Comparison of patients with SLE with RF seropositivity and RF seronegativity by main demographic, clinical and laboratory parameters
the time from the onset of clinical manifestations to establishing the diagnosis of SLE was significantly longer in RF-positive patients (2.0 years [0.5–3.0 years], p = 0.046) compared to patients with negative RF (0.5 year [0.3–1.9 years]). However, there was no significant difference in the frequency of misdiagnosis of RA between the groups (p = 0.364); all these cases were misdiagnosed, no one developed RA (Rhupus syndrome);
in SLE patients with RF seropositivity, kidney involvement (42.1% vs. 59.4%, p = 0.045) and fever (42.1% vs. 59.2%, p = 0.046) were less common compared to RF-negative patients;
the prevalence of lymphadenopathy was significantly higher in patients with SLE with the presence of RF (59.6%) compared to those with absence of RF (42.3%, p = 0.039);
among the routine laboratory parameters, CRP (7 mg/l [2–12 mg/l]) and ESR (23 mm/h [13–38 mm/h]) were significantly higher in patients with presence of RF than in the group with RF seronegativity (4 mg/l [2–9 mg/l]; p = 0.049 and 15 mm/h [9–28 mm/h]; p = 0.042, respectively);
patients with presence of RF had a higher ANA titer (1,280 [640–2,560] vs. 320 [320–1,000] [p = 0.04]) and were more frequently positive for antibodies to Ro/SSA (67.9% vs. 42.9% [p = 0.044]) and La/SSB (41.7% vs. 13,0% [p = 0.017]) compared to RF-negative patients;
no significant differences were found in the values of disease activity (SLEDAI-2K) and damage indices (SLICC/ACR DI), the concentration of complement components C3 and C4 and antibodies to double-stranded DNA and other nuclear antigens between patients with presence and absence of RF.
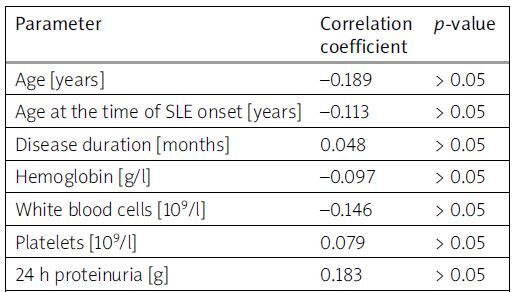
According to the results of the correlation analysis (Table II), a significant positive correlation was found between the concentration of RF and the levels of CRP (r = 0.318; p < 0.01) and ESR (r = 0.228; p = 0.04). These findings align well with the previously mentioned data regarding the association of RF seropositivity with elevated levels of inflammatory markers.
Table II
Correlations between serum levels of RF and particular clinical and laboratory parameters in patients with SLE
Also, no significant differences were found in the content of drug therapy used in SLE patients with the presence and absence of RF (Table III).
Table III
Drug therapy content in SLE patients with positive and negative RF
| Total number(n = 206) | SLE patients with presence of RF (n = 57) | SLE patients with absence of RF (n = 149) | p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Do not receive treatment [n (%)] | 34 (16.5) | 10 (17.5) | 24 (16.1) | 0.968 |
| Oral GCs [n (%)] | 165 (80.1) | 44 (77.2) | 121 (81.2) | 0.653 |
| Dose of GC (for prednisone) [mg/day] | 10 (5–20) | 10 (10–25) | 10 (7.5–20) | 0.398 |
| Aminoquinoline drugs [n (%)] | 111 (53.9) | 31 (54.4) | 80 (53.7) | 0.944 |
| Cyclophosphamide [n (%)] | 11 (5.3) | 4 (7.3) | 7 (4.8) | 0.727 |
| Mycophenolate mofetil [n (%)] | 20 (9.7) | 6 (10.9) | 14 (9.5) | 0.976 |
| Azathioprine [n (%)] | 15 (7.3) | 2 (3.6) | 13 (8.8) | 0.304 |
| Methotrexate [n (%)] | 11 (5.3) | 3 (5.5) | 8 (5.4) | 0.727 |
| Rituximab [n (%)] | 5 (2.4) | 1 (1.8) | 4 (2.7) | 0.905 |
In univariate logistic regression analysis (Table IV), it was found that the presence of RF was positively associated with lymphadenopathy (OR = 1.99 [1.07–3.71], p = 0.029), the presence of antibodies to Ro/SSA (OR = 2.81 [1.12–7.09], p = 0.028), and La/SSB (OR = 4.80 [1.54–14.9], p = 0.007), and negatively associated with kidney involvement (OR = 0.50 [0.26–0.94], p = 0.031).
Table IV
Univariate logistic regression analysis of factor variables independently associated with RF positivity in patients with SLE
Discussion
Our study on a Ukrainian contingent of SLE patients revealed that 27.7% of them were RF seropositive, aligning with literature data indicating that approximately every fourth patient with SLE has an elevated serum RF level [3]. It may be useful information for practicing physicians that patients with the presence of RF are diagnosed with SLE on average 1.5 years later compared to patients without an elevated RF titer. One of the possible reasons for the delay in diagnosis among RF-positive patients could be the initial diagnosis of RA, which was amended only with the emergence of specific manifestations (nephritis, serositis, cytopenias, central nervous system involvement) and laboratory confirmation of SLE. However, no significant difference in the frequency of misdiagnosis of RA was found in our patient cohort (p = 0.364). Furthermore, an elevated RF level in the presence of certain non-specific clinical manifestations (signs of sicca syndrome, Raynaud’s syndrome, lung involvement, etc.) could have been a reason for prolonged observation to rule out other systemic rheumatic diseases (pSS, MCTD, systemic sclerosis, etc.), especially in cases negative for the most specific antibodies for SLE – Ab-Sm and Ab-dsDNA. The higher frequency of lymphadenopathy we found in RF-positive patients might have required additional efforts and time to rule out oncohematological diseases, in which RF is also often detected. Another laboratory marker of RA, ACPA, was found to be elevated in 8.7% of our patients, consistent with results of other studies – 6.7% and 14.6% [9, 18]. Also, none of the studies revealed a connection between this parameter and the development of arthritis in SLE.
Among the identified associations with clinical manifestations of SLE, it should be noted that RF-seropositive patients exhibited a lower prevalence of lupus nephritis, consistent with previous literature data [4–7]. Potential mechanisms for this protective effect include the competition of RF with components of the complement system for binding to immune complexes, thus slowing down their further deposition in the renal glomeruli, as well as the acceleration of the elimination of immune complexes bound to RF by the reticuloendothelial system [3, 7].
From a clinical point of view, it is important to note that according to the obtained results, RF-seropositive patients exhibited higher levels of ESR and CRP. The significant direct correlation between RF concentration with CRP and ESR further confirms their synergistic nature as markers of inflammatory process activity. It is noteworthy that a higher level of ESR and CRP in RF-positive patients is also characteristic of ANCA-associated vasculitis [19], but not characteristic of RA [20, 21].
In addition to markers of inflammation, elevation of RF level was also associated with a higher titer of ANA, positivity for antibodies to Ro/SSA and La/SSB antigens. Previously, it was found that only IgA class RF correlated with the level of antibodies to Ro/SSA and La/SSB in patients with SLE [4]. Studies among patients with pSS have found a correlation between RF concentration and all three of the above-mentioned parameters [4]. The obtained data may indicate an association between RF level and the overall antibody-producing activity of B-lymphocytes [4, 22], although the connection with the production of antibodies specifically to Ro/SSA and La/SSB remains poorly understood. Logistic regression analysis demonstrated an independent association between RF positivity and the development of lymphadenopathy, lupus nephritis, and the presence of antibodies to Ro/SSA and La/SSB in our patients.
However, despite the aforementioned associations of RF with inflammatory markers and autoantibodies, no direct relationship with the activity index (SLEDAI-2K), as well as the concentration of complement components C3 and C4 and antibodies to double-stranded DNA, was found. There was also no association between RF levels and some clinical manifestations and laboratory parameters that were found in previous studies, including serositis, hematologic disorders, malar rash, positivity for antibodies to Smith antigen, APLA, and the incidence of antiphospholipid syndrome [4, 5, 8]. The relationship between RF and lymphadenopathy and fever, as found in our study, has not been described in the literature and warrants further investigation. According to the obtained data, there was no significant relationship between the serological status for RF and the value of the SLICC/ACR DI or pharmacological treatment.
As RF positivity is associated with higher levels of ESR, CRP, and ANA, such patients are generally expected to be treated more aggressively. Surprisingly, no significant difference in treatment was found between RF-seropositive and -seronegative patients despite existing differences in clinical and laboratory characteristics. One of the causes could be the lower prevalence of lupus nephritis in the RF-seropositive group, which allows doctors to use less aggressive treatment options. Moreover, even though RF-seropositive patients have higher levels of ESR, CRP, ANA, their SLEDAI-2K index does not differ significantly from RF-seronegative patients, whereas disease activity, along with the organ involvement pattern, is the most important factor in choosing the treatment strategy.
Limitations
It should be noted that our study has several limitations. The analysis of clinical and laboratory data was conducted during patient visits to specialized rheumatological institutions, which could have led to an underestimation of the frequency of some abnormalities that were not detected and/or recorded at the primary stages of medical care. Additionally, the majority of patients were already receiving GCs at the time of data collection, which likely influenced hematological parameters, particularly the level of inflammatory markers. Furthermore, unlike ANA, antibodies to individual autoantigens were not determined in all patients, which could have affected the results obtained.
Conclusions
In RF-seropositive SLE patients (approximately 28%), the diagnosis is established later compared to RF-seronegative ones; kidney involvement and fever are less common, while lymphadenopathy develops more frequently. RF seropositivity is associated with higher levels of ESR, CRP, ANA, and the presence of antibodies to Ro/SSA and La/SSB. However, the RF level does not correlate with the SLEDAI-2K, SLICC/ACR DI and the frequency of joint involvement. According to the results of univariate logistic regression analysis, an independent association with RF positivity was confirmed only for kidney involvement, lymphadenopathy, and antibodies to Ro/SSA and La/SSB.