Introduction
Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA), formerly known as Churg-Strauss syndrome, is a rare form of anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV). It is characterized by eosinophil-rich granulomatous inflammation and vasculitis affecting small to medium-sized vessels [1, 2]. The incidence of EGPA varies from 0.5 to 6.8 cases per million per year, accounting for up to 21.4% of AAV cases in European countries [3]. The average age of diagnosis is between 40 and 50 years with no sex predominance [4]. This disease is marked by diverse clinical manifestations and varying organ involvement [5].
Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis typically progresses through three distinct stages: 1) the allergic stage, characterized by symptoms like asthma, allergic rhinitis, and sinusitis; 2) the eosinophilic stage, which may last up to 8–10 years and is marked by hypereosinophilia and eosinophilic infiltration of tissues; and 3) the vasculitic stage, characterized by systemic vasculitis [3, 4]. However, these phases do not always occur sequentially, may overlap, and some patients may never develop vasculitic complications [4].
Although EGPA is classified as a subtype of AAV, only about half of EGPA cases are ANCA-positive [5]. In most ANCA-positive EGPA cases, a perinuclear ANCA pattern is observed through indirect immunofluorescence, primarily associated with anti-myeloperoxidase (MPO-ANCA) antibodies [4]. Despite the existence of two main forms of clinical involvement based on ANCA status, the reported frequencies of EGPA symptoms can be inconsistent [5].
Given the variability in its clinical presentation, diagnosing EGPA is challenging. No single feature of the disease is pathognomonic. Furthermore, EGPA often presents in phases, with both clinical symptoms and pathological findings varying depending on the anatomical site affected and the stage of the disease.
Material and methods
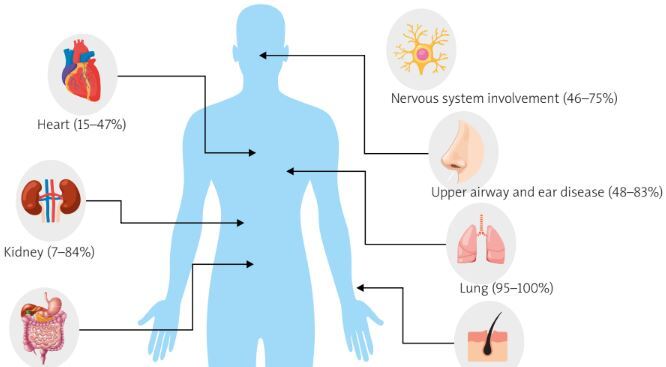
The authors analyzed SCOPUS, MEDLINE and PubMed medical databases between 2000 and until August 2024 using the following key words: eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, EGPA, ANCA-associated vasculitis, AAV. Filters applied: full text, books and documents, clinical study, clinical trial, guideline, meta-analysis, multicenter study, observational study, practice guideline, review, systematic review. Only full-text studies in English were analyzed. The databases were searched according to the division into eight main clinical subsections (Fig. 1). After excluding duplicates and studies of poor quality and content, 42 articles were used to review clinical features. Only full-text studies in English were analyzed.
Results
Diagnostic criteria
The clinical manifestations of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) are not easily distinguished from those of other systemic diseases in the early phase, and the incidence of serious complications or all-cause mortality is as high as in chronic diseases in refractory cases [6]. The diagnosis of EGPA is based on the 2022 American College of Rheumatology (ACR)/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) classification criteria (Table I) [6, 7].
Table I
Classification criteria for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, based on [8]
All other disease states that may cause similar symptoms must be excluded, especially other AAV syndromes (GPA, MPO) and hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES). Hence, the differential diagnosis of EGPA includes evaluation for other causes of hypereosinophilia, especially local eosinophilic diseases involving the respiratory tract (e.g., allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis and chronic eosinophilic pneumonia) or the gastrointestinal tract (e.g., eosinophilic gastroenteritis, parasitic infections) [10, 11]. Distinguishing EGPA from HES can be challenging, particularly in cases without overt vasculitis manifestations and without detectable ANCA [12]. Similarities in clinical presentation mean that exclusion of HES variants or identification of overlapping HES in some cases is only possible based on bone marrow biopsy or trepanobiopsy and/or genetic testing for the presence of the FIP1L1-PDGFRA fusion gene. This gene, resulting from the deletion of a fragment of chromosome 4 and encoding a protein with tyrosine kinase activity, occurs in chronic eosinophilic leukemia (CEL) [13]. Several cytokines have been studied as potential biomarkers of HES and EGPA (including serum interleukin-8 [IL-8], IL-5, IL-10, CC chemokine ligand 17 [CCL17], initially named named TARC [thymus- and activation-regulated chemokine]), but they cannot clearly distinguish between these diseases [14]. However, normal C-reactive protein (CRP) values have been found to be suggestive of HES compared with EGPA in patients with asthma, eosinophilia, and systemic signs of tissue hypereosinophilia [15]. Tables II and III summarize the differences between EGPA and these diseases.
Table II
[i] According to the 2022 ACR/EULAR, the following number of points are required for recognition: EGPA ≥ 6, MPA and GPA ≥ 5.
[ii] AAV – anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis, cANCA – cytoplasmic ANCA, EGPA – eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, GPA – granulomatosis with polyangiitis, MPA – microscopic polyangiitis, MPO-ANCA – myeloperoxidase-specific antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody, pANCA – perinuclear ANCA, PR3-ANCA – proteinase 3-ANCA.
Table III
Differences between HES and EGPA based on [16]
Clinical features
Lung involvement
Most patients with EGPA develop symptoms of late asthma (95–100%) [1]. The diagnosis of asthma usually precedes the diagnosis of EGPA by 3–9 years [17], and about half of patients experience severe or uncontrolled asthma symptoms that may require high doses of glucocorticosteroids (GCs) to maintain disease control [18]. Eosinophilic pneumonia is relatively common in patients with EGPA but may be underdiagnosed due to mild clinical symptoms and corticosteroid therapy [19]. Hypereosinophilic bronchiolitis, characterized by bronchiectasis and airway abnormalities such as centrilobular nodules and bronchial wall thickening, may also be observed [20]. In EGPA, asthma is often associated with chronic rhinosinusitis (80%), atopy (25%), blood eosinophilia (up to 95%), and positive ANCA (10–40%), with antibodies often directed against the MPO antigen [21]. Imaging studies may reveal abnormalities such as peripheral ground-glass opacities, consolidations, bronchial thickening, or pleural effusions, while pulmonary function tests reveal airway obstruction with bronchodilator response and preserved or increased diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide [22]. Histopathological findings of pulmonary nodules biopsies may show eosinophilic necrosis, while a high percentage of eosinophils in the bronchoalveolar lavage differential cell count indicates eosinophilic pneumonia as a manifestation of EGPA [21, 23]. Lung fibrosis is very rare in EGPA.
Heart involvement
Cardiac involvement is already evident early in EGPA and is strongly associated with eosinophilia [24]. It is usually an early manifestation, but it can also occur later in the course of the disease. Patients may develop myocarditis, heart failure, pericarditis, tamponade, and myocardial infarction, most of which are associated with a poor prognosis [25].
Eosinophilic myocarditis (known as Loeffler’s myocarditis, endocarditis) is the most common form, which can lead to left ventricular dysfunction, aneurysms, and thrombosis events [25]. Approximately 27% to 47% of patients with EGPA have symptomatic cardiac involvement, with a higher incidence in the ANCA-negative population [26]. Some patients may eventually develop symptoms of restrictive or dilated cardiomyopathy as a result of inflammation of the heart muscle, leading to permanent impairment of left ventricular function. Furthermore, in the course of EGPA, the coronary arteries may be affected, manifesting as stenocardial symptoms [25]. Approximately 15–20% of patients with EGPA with cardiovascular involvement develop acute pericarditis, which may be complicated by significant pericardial effusion and tamponade [25].
In each case of EGPA, it is necessary to consider performing a screening test for cardiac involvement, e.g. laboratory tests for cardiac troponin T and troponin I and/or N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide. This ensures that asymptomatic patients, who constitute about 40% of patients, are not missed [27]. The recommended imaging test for EGPA is cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), due to its sensitivity and repeatability. A dedicated MRI protocol included functional analysis, and pre- and post-contrast tissue characterization [28].
Due to the wide heterogeneity of cardiac involvement in EGPA, it is crucial to identify the high-risk population. In a recent study by Liu et al. [27], patients were divided into three groups based on cardiac enzymes, MRI, and endomyocardial biopsy: eosinophilic myocarditis (EGPA-EM), chronic inflammatory cardiomyopathy (EGPA-ICM), and EGPA-control. Finally, the prognosis of EGPA-EM was significantly worse, with a mortality rate of 14.86% and a 2-year event-free survival rate of less than 50%. Moreover, the authors proposed the LATE-EAST diagnostic algorithm. The algorithm includes: absence pulmonary infiltrates (score 0.5), negative ANCA antibodies (score 0.5), eosinophil count (score 0.5: > 6.38 × 109/l or score 1: > 9.91 × 109/l), cardiac troponin I level (score 1: > upper limit of normal or score 2: > 1.90 ng/ml), left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), % (score 1: < lower limit of normal or score 2: < 40.00%), ST-T segment abnormalities (score: 1) and myocardial edema (score 2). Patients with overall scores > 4.3 are EGPA-EM patients. Overall prediction accuracy was 83% [27].
Skin involvement
Skin involvement is a common feature of the vasculitic phase of EGPA, occurring in 39.7% to 81% of cases [1, 29, 30]. Cutaneous lesions are more frequently observed in EGPA than in GPA when blood eosinophil levels are normal [5]. The available literature does not provide a definitive answer on whether ANCA-positive patients are at a higher risk of developing skin changes compared to ANCA-negative ones during the course of EGPA [5]. Palpable purpura, a key cutaneous manifestation, affects approximately 50% of patients and is often localized on the limbs and scalp [29, 30]. Other skin changes observed in EGPA include subcutaneous nodules, papules, macular/papular/maculopapular rashes, ecchymoses, petechiae, and hemorrhagic bullae [1]. Less commonly observed manifestations include urticaria, livedo reticularis, and erythematous macules [1, 30]. Histopathological examination of skin biopsies often shows vasculitis, eosinophil infiltration, and extravascular granulomas, though these findings rarely co-occur in a single specimen [30]. Typically, skin biopsies reveal leukocytoclastic vasculitis with eosinophil infiltration [31]. In ANCA-positive EGPA, skin manifestations typically present as hemorrhagic lesions, often appearing as palpable purpura, or as dermal and subcutaneous nodules and papules [5]. Excluding eosinophil count from the relapse model, ANCA positivity and cutaneous signs at diagnosis emerge as the most significant predictors of future relapses [29].
Upper airway and ear disease
Otolaryngologic manifestations are reported in 48% to 83% of patients with EGPA. These manifestations commonly include rhinitis, sinusitis, nasal polyposis, and nasal obstruction, with rarer occurrence of otitis media [29, 32, 33]. Furthermore, ear/nose/throat symptoms are more frequently observed in patients who are ANCA-positive compared to those who are ANCA-negative [5, 29]. Chronic rhinosinusitis is a prevalent issue in EGPA patients, with common presenting symptoms including nasal discharge, followed by nasal congestion, and facial pain and pressure [33]. Computed tomography scans of the paranasal sinuses in EGPA patients reveal significant variation in total Lund-Mackay staging (LMS) scores, indicating considerable heterogeneity in the severity of sinus lesions [34]. While patients with EGPA and low LMS scores exhibit only minor abnormalities in the maxillary and anterior ethmoid regions, those with higher LMS scores are notably affected in the ostiomeatal complex [34]. Interestingly, the prevalence of a Five-Factor Score (FFS) ≥ 2 and cardiac involvement is significantly greater in patients with EGPA who have low LMS scores [34]. Nasal polyposis is particularly common, occurring in more than half of EGPA patients [35]. Ear involvement in EGPA was reported to be statistically significantly associated with the vasculitic pattern of the disease and independent of nasal impairment, cytology, and the duration of nasal symptoms [32]. Approximately 8% of EGPA patients experience varying degrees of hearing loss, including sensorineural hearing loss, mixed sensorineural and conductive hearing loss, presbycusis, and otitis media with effusion. Additionally, vestibular impairment in EGPA is characterized by benign paroxysmal positional vertigo and non-specific dizziness [32].
Gastrointestinal system
The involvement of the gastrointestinal (GI) system in EGPA is reported with highly variable frequency, ranging from 20% to 89% of cases [36, 37]. Gastrointestinal manifestations are more common in EGPA compared to GPA when blood eosinophilia is within normal levels, though this is not the case when GPA is accompanied by elevated blood eosinophilia [5]. The occurrence of GI symptoms is more prevalent in ANCA-negative EGPA patients than ANCA-positive patients [5]. Among ANCA-positive patients, those who are pentraxin-3 (PTX-3) positive more frequently have GI involvement [38]. When comparing EGPA patients with GI involvement to those without, patients with GI involvement demonstrate higher levels of high-sensitivity CRP, a higher Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (BVAS), and a higher FFS. Additionally, these patients are more likely to experience weight loss at the baseline [37]. Among the GI symptoms reported in EGPA patients, abdominal pain (90.5%) and diarrhea (42.9%) are the most common. Furthermore, symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, GI perforation, GI bleeding, and melena are relatively common in these patients [37]. Weight loss is also identified as a potential risk factor for GI involvement in EGPA patients [37]. During follow-up, patients with GI involvement in EGPA show a lower cumulative survival rate, a lower long-term remission rate, and a higher cumulative relapse rate when compared to those without GI involvement [37, 39]. However, no significant differences were found between EGPA patients with or without GI involvement concerning age, organ involvement, baseline treatment, eosinophil count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), or serum IgE levels [37]. Gastroscopic findings in EGPA patients with GI involvement most commonly reveal nonulcerative gastritis, which is present in the majority of these cases [37]. Duodenitis is also observed with relatively high incidence, while colitis is the most frequent finding identified through colonoscopy [37]. In summary, the stomach is found to be the most commonly affected GI organ. Given that GI involvement is a significant risk factor for poor prognosis and a leading cause of death in EGPA patients, aggressive medical treatment and surgical intervention are recommended when indicated [37, 39].
Kidney involvement
The frequency of kidney involvement in EGPA varies among studies, ranging from 7% to 84% [40, 41]. However, the majority of the literature indicates that kidney involvement is more prevalent in GPA and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) [4, 42]. In contrast, kidney involvement in EGPA is more often associated with the ANCA-positive phenotype, occurring in up to 84% of these cases [3, 4, 42]. Among those with ANCA-positive kidney involvement, anti-MPO antibodies are the most frequently detected [42]. Additionally, ANCA-positive EGPA patients are reported to have more severe renal damage [3]. Renal manifestations of the disease vary widely. While the majority of patients exhibit mild urinary abnormalities, a subset experiences severe, rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis, necessitating dialysis [3]. The most frequent histological manifestation of EGPA is necrotizing pauci-immune glomerulonephritis, confirmed in approximately 78% of patients [3, 4]. Most EGPA patients with rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis display a focal or crescentic histological class, suggesting that renal involvement is usually detected early. This contrasts with MPA patients with anti-myeloperoxidase (anti-MPO) antibodies, where renal involvement is often diagnosed at more advanced stages [4]. A useful method for predicting renal outcomes and enabling early end-stage renal disease risk prediction is a clinically applicable renal risk score for ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis, which emphasizes the importance of unaffected glomeruli [42, 43]. Membranous nephropathy (10%) and membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (3%) are predominantly observed in ANCA-negative patients [42]. Predominant eosinophilic infiltration is present in the histopathological results of kidney biopsies in only 10% of patients [4].
Nervous system involvement
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) involvement is reported in 46.4–75% of EGPA patients, whereas central nervous system (CNS) involvement is less common, occurring in 5–17.3% of cases [44–46]. Neurological manifestations, central or peripheral, can be the initial presentation in up to 62% of EGPA cases [44]. The frequency of MPO-ANCA positivity with peripheral nervous symptoms is significantly higher than in those without, with no significant difference in blood eosinophil levels between the two groups, suggesting that PNS involvement in EGPA is primarily due to ANCA-mediated vasculitis rather than eosinophil-related infiltration [38, 44]. Similarly, PTX3-ANCA positive patients also show a higher prevalence of PNS manifestations (80% vs. 48.5%) [38]. Although the prevalence of PR3-ANCA positive EGPA patients is low (2.2%), these patients also display a higher prevalence of PNS signs [38]. Additionally, EGPA patients with a baseline BVAS score greater than 15 are more likely to develop PNS symptoms [45]. Mononeuritis multiplex, often severe and sensorimotor in nature, is the classic and more common presentation compared to acute symmetrical polyneuropathy [1, 44]. Electrophysiological studies indicate that axonal injury tends to progress as mononeuritis multiplex, potentially leading to foot or wrist drop, though it can also present as asymmetrical or symmetrical polyneuropathies, with sensory deficits or neuropathic pain [1]. Sural nerve biopsies have revealed epineural necrotizing vasculitis, likely causing ischemic nerve injury and subsequent neuropathy [1]. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis patients with PNS involvement are more prone to weight loss, arthritis, increased ESR, and elevated CRP and rheumatoid factor (RF) levels, but do not show significant differences in vital organ involvement (lungs, kidneys, CNS, heart, or gastrointestinal system) compared to those without PNS involvement [45]. MPO-ANCA and PTX3-ANCA positive EGPA patients also exhibit more frequent CNS involvement than those who are ANCA-negative [38]. Central nervous system manifestations in EGPA are diverse, potentially affecting all CNS regions and presenting as ischemic lesions, posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, intracranial hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, or spinal cord involvement [46, 47]. Compared to EGPA, GPA is more associated with chronic hypophysitis, while MPA is predominantly linked to cerebrovascular neuropathy [46]. Age, disease duration, and fever are independent factors associated with CNS manifestations in EGPA [46, 47]. Notably, patients with CNS involvement are also more likely to experience digestive tract issues [47].
Thromboembolic events
The occurrence of arterial and venous thrombotic events (AVTE) in EGPA patients ranges from 8.2% to 36% [48–50]. The prevalence of AVTE slightly increases after EGPA diagnosis, with 12.4% of patients experiencing AVTE episodes both before and after diagnosis [49]. Most AVTE cases are diagnosed within two years of the initial diagnosis, peaking during periods of high disease activity [48, 49]. Arterial thrombotic episodes are diagnosed more frequently than venous ones, with acute myocardial infarction and deep vein thrombosis being the most common in their respective categories. However, venous events have higher age-standardized event ratios in the EGPA cohort compared to the reference population [49]. The AVTE frequency in EGPA is similar to other ANCA-associated vasculitides such as GPA and MPA, but higher than in polyarteritis nodosa [48].
The AVTE risk is significantly higher in patients with a history of AVTE or a BVAS of 20 or more at diagnosis, compared to those with a BVAS of 0–9 [49]. Additionally, patients who do not receive immunomodulating therapy within the first two months after the diagnosis have a 3.67-fold higher risk of AVTE compared to those treated with systemic GCs. The AVTE risk is similar in patients treated with immunosuppressants or GCs alone [49]. No association has been found between antiplatelet, anticoagulant, or statin therapy at diagnosis and AVTE risk [49]. Histopathological findings of thrombotic features in dermal or subcutaneous vessels and elevated plasma D-dimer levels (> 2.5 μg/ml) are predictive factors of AVTE in EGPA [50].
Diagnostic methods for AVTE in EGPA are similar to those used in the general population, including echocardiography, computed tomography angiography, and coronary angiography [49, 51–54].
To summarize, EGPA is less often diagnosed than other AAV, and the differential diagnosis with other diseases with an eosinophilic state should be excluded. All organs and systems can be affected, but especially the upper and lower respiratory tract, skin or kidney involvement may dominate. Eosinophilia alone is not always a reliable sign, and previous GCs therapy before the final diagnosis may obscure the clinical picture.
Undoubtedly, analysis of each case, manifestation of organ involvement and suspicion of disease from the AAV group such as EGPA require a particularly broad and multidisciplinary diagnostic approach.
Here we have not discussed the treatment of EGPA. However, this issue will be addressed comprehensively in a separate paper. Expanding knowledge about the pathogenesis of this disease and development of tools/methods of diagnosis have allowed for simultaneous expansion of therapeutic possibilities, including biological ones, thus requiring a extensive presentation.
Conclusions
This review offers valuable and comprehensive insights into the demographic, clinical, and laboratory characteristics of patients with EGPA. We emphasize the diverse clinical phenotypes observed (Fig. 2), particularly those associated with eosinophilic manifestations and vasculitic symptoms.