Introduction
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a multi-organ disease characterized by disruption of the morphology and function of small blood vessels, with non-specific inflammation, activation of the immune system and progressive fibrosis of the skin and internal organs. The aetiopathogenesis of SSc is not precisely known. Musculoskeletal involvement affects approximately 46–95% of SSc patients [1]. During the disease, any structure of the musculoskeletal system, such as bones, joints, tendon sheaths, tendons and muscles, may be affected (Table I) [2, 3]. Most often, however, the changes affect the hands, which leads to a deterioration of the quality of life and disability of patients.
Table I
Musculoskeletal involvement in systemic sclerosis
Pathogenesis
A large role is attributed to genetic predispositions and environmental factors that induce three different processes: endothelial damage, activation of the immune cells and fibroblast function disorders. The earliest changes occur in the morphology of small vessels, known as scleroderma-associated microangiopathy, which is associated with activation and damage of vascular endothelial cells, marked by increased levels of vasoconstrictors such as endothelin-1 (ET-1), thrombomodulin, and thromboxane and reduced levels of nitric oxide and prostaglandin I2. Endothelial cells release excessive amounts of several biologically active substances, including vasoconstrictive, pro-angiogenic and pro-fibrotic factors, as a result of which the immune cells and fibroblasts are stimulated, which leads to vasoconstriction, inflammation in the perivascular space, and fibrosis. Vasospasm and proliferation of damaged endothelial cells, as well as progressive fibrosis of the intima and media of the vessel, lead to narrowing and even closure of the vessel lumen (obliterative vasculopathy), resulting in tissue ischaemia. Recurring vascular ischaemia plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of hand pathology observed in SSc. Up to 95% of SSc patients are affected by Raynaud’s phenomenon, distinctive for discolouration of the fingers (typically from white to blue then red) with numbness and pain, often presenting as the first symptom. The fibroblast defect leads, in turn, to deposition of collagen and extracellular ground substance that leads to organ and tissue fibrosis. The consequences of vascular and immunological disorders and fibrosis are serious organ complications. During the disease, any organ may be affected; however, the most common changes are visible in the lungs, heart, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, skin, and the musculoskeletal system [4–7]. Musculoskeletal involvement represents a significant contributor to disability, encompassing a range of conditions such as arthralgia, arthritis, tendinitis, finger contractures, acro-osteolysis, calcinosis of tissues and myopathy.
Joint pain in systemic sclerosis
Joint changes in SSc are quite a common manifestation of the disease and mainly affect the joints of the hands, leading to irreversible damage. The most common symptom is joint pain (arthralgia). Data on the incidence of arthralgia are divergent and range from 38 to 97% [8–10]. Joint symptoms may precede the onset of SSc, appear together with other manifestations, or be the first symptom of the disease. In one study, 38 patients with SSc were examined, 2/3 (66%) of whom had joint manifestations during the disease, and as many as half of them had symptoms before the diagnosis of SSc [11]. In another, 12-month prospective, study, 76 patients with SSc were examined and joint pain was found in 38%, in most cases in limited SSc [12]. In the Canadian Registry of SSc Patients with surveys conducted among 464 patients, joint pain was the fourth (out of 69) most common reported manifestation of the disease, and the severity of pain moderately or even significantly influenced the patients’ daily life activity [13]. Generally, in approximately 20% of patients with SSc joint pain precedes the onset of the disease by approximately 1 year; in 30% it occurs during the diagnosis, and in 50% after the diagnosis of SSc. Moreover, approximately 50% of SSc patients describe the pain as moderate or severe [11]. In a study involving 38 SSc patients, Baron et al. [14] found that 66% of patients had joint symptoms, of which 61% had symmetrical polyarticular symptoms, 22% had oligoarticular symptoms, and 17% had one affected joint. In 40% of cases, the symptoms had a sudden onset and in 60% they were progressive. The nature of the symptoms was transient in 44% of patients, chronic in 16% yet with partial remissions, slowly increasing over time in 36%, while in 4% the symptoms progressed rapidly [14].
Arthritis in systemic sclerosis
Inflammation of joints and tendon sheaths is observed in 13–40% of SSc patients, especially in the diffuse type of the disease. The incidence depends on how the arthritis was assessed, whether it was a physical examination of the joint or radiological imaging, such as ultrasound or magnetic resonance [11, 15]. In SSc, arthritis most often affects the small joints of the hands, but other joints may also be affected, even the temporomandibular joints. In patients with a shorter disease duration (less than 3 years), a meta-analysis of five studies showed that clinically confirmed arthritis was found in 23% of patients with SSc, and radiological changes in 26% of patients [1]. In another prospective study involving a group of 120 patients with SSc, 18% had arthritis, assessed radiologically as the presence of erosions and joint space narrowing [16]. La Montagna et al. [12] have found arthritis in 13% of patients with SSc, assessing the minimum distance between the middle finger and the palmar surface. In the German Patient Register, 1,483 patients with SSc were examined. Arthritis, assessed as swelling and tenderness to pressure in at least one joint, was found in 47.5% of patients, where, most frequently, the number of painful joints was 3, and the number of swollen joints was 1–2 [17]. In the European Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) group of 7,286 patients, arthritis was demonstrated in 15% of patients [18].
According to literature data, erosive arthritis in SSc correlates with the duration of the disease, the extent of skin lesions, fingertip ulcers, resorption of the distal phalanges, and increased CRP concentration [11, 15, 19, 20]. Avouac et al. [21] studying a group of 1,301 patients with SSc lasting less than 3 years found that arthritis is an independent factor worsening the degree of skin involvement, the occurrence of new fingertip ulcers, cardiac involvement and disease progression; moreover, arthritis was found to be associated with more frequent development of pulmonary arterial hypertension and muscle involvement.
The incidence of arthritis and tendon sheath inflammation in SSc depends on imaging methods. The tests used in the diagnosis of inflammation of joints and tendon sheaths in SSc include radiographs, joint ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Eihai et al. [22] examined 52 patients with SSc, finding arthritis of the hands in 15% of patients on physical examination and in as many as 46% of patients during ultrasonographic examination of the hands. Furthermore, tenosynovitis was observed in 6% of patients during physical examination vs. 27% in ultrasound examination. In another study, Cuomo et al. [23] have demonstrated that in a group of 45 patients with SSc, the incidence of arthritis (effusion and synovial hyperplasia) in ultrasound examination was much higher, compared to the physical examination (58% vs. 33%). Ultrasonography revealed joint effusion in 42% of patients with SSc, and hypertrophy and vascularization of the synovial membrane were minor, compared to the group of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In yet another study, Fairchild et al. [24] performed joint ultrasound in 43 patients with SSc, observing involvement of the synovial membrane of joints in 18.6% of them. Moreover, according to Hubac et al. [25], who performed ultrasonography of hand joints in 55 patients with SSc, the ultrasound examination was a sensitive method for detecting inflammation of joints and tendon sheaths, while the involvement of hand joints was more common than that of feet joints in SSc, and the inflammation of only one hand joint correlated with a diffuse subtype of the disease and limited hand function. Another method used in the diagnosis of arthritis is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of joints, which is a more sensitive test than US, although technically more difficult to perform. In one study the authors performed MRI of hand joints in 17 patients with SSc, finding inflammation of joints and tendon sheaths in as many as 59% of them [26]. In another study, Chitale et al. [27] performed ultrasound of hand joints in 13 out of 17 patients with SSc and joint pain without clinical signs of inflammation, who were randomly selected regardless of the severity of pain. The authors performed MRI of joints in 8 out of 17 patients who had the most severe hand joint symptoms. In the examined group of patients, arthritis was detected by ultrasound in 46% and by MRI in 100%. According to literature data, bone erosions were found in approximately 5–40% of patients with SSc [11]. In their study, Abdel-Magied et al. [28] found that patients with joint pain without clinical signs of arthritis suffered from inflammatory erosive hand arthropathy, detected by joint ultrasound and MRI. By analysing radiological models, 3 forms of joint involvement were identified in patients with SSc. The first, most common model (60–70% of cases) is SSc arthropathy, with finger contractures. Radiologically, it is a periarticular fibrosing pattern, manifested in X-rays of the hand joints by narrowing of the distal interphalangeal joint spaces. The second one is an inflammatory model of joint involvement, resembling rheumatic disease, manifested in hand X-rays by osteoporosis of bone metaphyses, narrowing of the spaces of the proximal interphalangeal joints, wrists, and the presence of erosions of the epiphyses of the bones forming the joints of the wrists, metacarpophalangeal joints and proximal interphalangeal joints, accounting for approximately 15–20% of cases. The third one, approximately constituting another 15–20% of cases, is a degenerative model of joint involvement, characterized in hand X-rays by narrowing of the proximal and distal interphalangeal joint spaces, subchondral sclerosis and the presence of osteophytes [11, 12]. Erre et al. [29] additionally distinguished a fourth model, i.e. one of minimal changes, where the radiological image is normal or there is an isolated narrowing of the space of the distal interphalangeal joint of the hand. According to La Montagna et al. [12], the most common model in the hand area is the fibrosing model, while the inflammatory and degenerative model accounts for approximately 13%; in the feet, the degenerative model is most frequently found, while the inflammatory model accounts for approximately 7% and the fibrosing model for 8% of cases.
In one study Sinziana et al. [30] examined 159 patients with very early SSc (defined as presence of Raynaud’s phenomenon and/or at least one of: puffy fingers, presence of ANA, abnormalities in capillaroscopy or not fulfilling EULAR/ACR classification criteria for SSc at baseline). Out of 159 patients 22 manifested SSc-related arthritis, with more than a half needing treatment with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Anti-centromere antibodies (ACA) were negatively associated with arthritis as they are associated with a limited subtype of the disease.
Rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) are marker antibodies for RA, but their presence can be detected in SSc. Rheumatoid factor occurs in approximately 30–40% of patients with SSc [31]. The incidence especially increases in patients with secondary Sjögren’s syndrome. It has been shown that the presence of RF in SSc patients does not correlate with erosive arthritis, but joint pain is more common in this group of patients [32]. However, the presence of ACPA in SSc may suggest SSc/RA overlap syndrome and precede the occurrence of erosive arthritis. The ACPA occur in approximately 10–12% of patients with SSc [31, 33]. Studies regarding the relationship between ACPA antibodies and erosive arthritis in SSc are controversial. Avouac et al. [34] did not detect a relationship between ACPA and the presence of erosive arthritis in patients with SSc. In turn, a meta-analysis of 13 studies showed that ACPA increases the risk of developing erosive arthritis, pulmonary fibrosis, oesophageal involvement and diffuse SSc [35]. Kamalaksha et al. [31] also found, in a registry of 132 patients from New Zealand, that ACPA correlates with arthralgia and the presence of erosions in patients with SSc, while RF only correlates with arthralgia.
Tendon involvement in systemic sclerosis
Pathological changes in SSc may occur within tendon attachments to the bones (enthesopathy) and the tendons themselves. Terenzi et al. [36] performed an ultrasound examination among 100 patients with SSc and 25 healthy volunteers, revealing that enthesitis with the presence of calcifications and enthesophytes occurred significantly more often in patients with SSc. Inflammation of the insertions of finger extensor tendons was most frequently observed [36]. In SSc, inflammation of tendons and tendon sheaths and even tendon rupture may also occur. It has been reported that in SSc the inflammation of tendons and tendon sheaths in ultrasound examination is characterized by less severe inflammation, compared to patients with RA, while the dominant process is severe fibrosis (sclerosing tenosynovitis). In 50% of cases, ultrasound-detected tendonitis coexists with arthritis in SSc. The hand tendons are most often affected, first the extensors and then the finger flexors. Tendon lesions, more often occurring in the diffuse form of SSc, have been found to correlate with the serological profile of the disease, especially with anti-RNA polymerase III antibodies [11, 37]. One of the more serious complications of fibrosing tendonitis and tendon sheath inflammation during SSc is tendon rupture, which affects approximately 10% of patients [37]. Tears most often affect the tendons of the fingers, wrists, knees, ankles and elbows, but they can occur in any location [38]. It has also been found that tendon friction and ruptures mainly concern the diffuse form of SSc, especially in the initial phase of disease, and correlate with a more severe course of SSc, the development of scleroderma renal crisis, and severe involvement of the gastrointestinal tract [20, 39, 40]. In the European EUSTAR registry examining 1,301 patients with SSc, tendon ruptures have been found to be a factor of rapid progression of the disease. Moreover, they may be a risk factor for the development of fingertip ulcers, progression of skin lesions, and the development of heart failure [21].
Contractures of fingers in systemic sclerosis
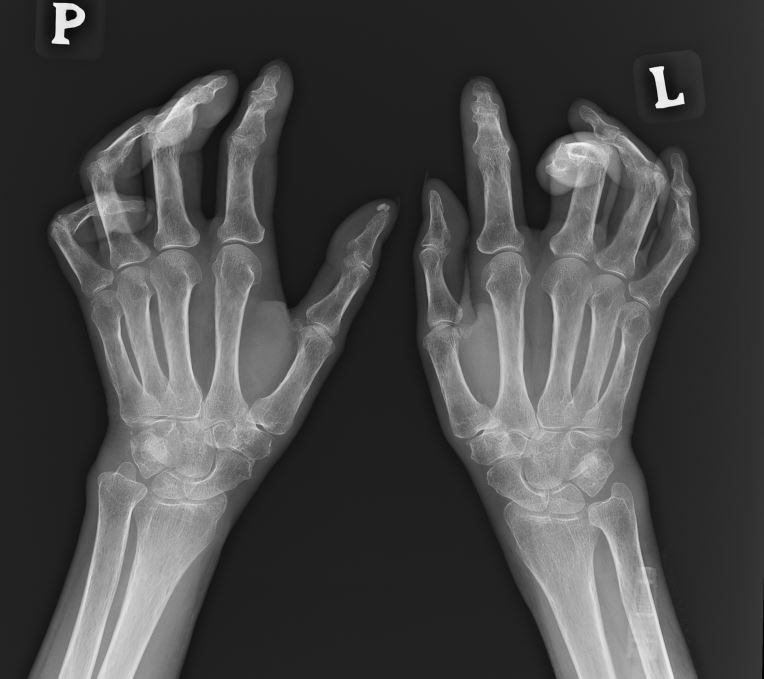
Flexion contractures of fingers are among the main causes of disability in patients with SSc (Fig. 1). They occur in 1/4–1/3 of patients with SSc (approximately 31%), most often in the second and third fingers of the hand. Radiologically, they are changes in the form of periarticular fibrosis (SSc arthropathy). Finger contractures in SSc are more common in the diffuse form of the disease. In this subtype, impairment of hand function is more rapid, and in more than half of patients it occurs within the first 18 months of disease onset. Hand deformities have been found to correlate with the degree of involvement of internal organs, especially with interstitial lung disease and oesophageal involvement, and may also precede the development of scleroderma renal crisis. Moreover, flexion contractures of fingers are more often observed in patients with anti-topoisomerase I antibodies and correlate with increased C-reactive protein values. It has also been reported that calcifications in soft tissues and vascular changes in the form of fingertip ulcers may precede the occurrence of contractures [11, 19]. Furthermore, a higher degree of skin sclerosis and impairment of flexion and extension of fingers was observed in the dominant hand compared to the other hand [41]. Deformities of hand joints lead to significant impairment of hand function, difficulties in performing everyday life activities, and, consequently, deterioration of the quality of life and disability of patients. Various tools are used to assess hand function, including the Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI), the hand anatomical index, calculated on the basis of the difference between the total range of the open hand and the closed hand, divided by the lateral length of the hand, as well as the finger-to-hand index, which is the difference between the distance of the third finger and the surface of the hand when the fingers are straight and when the fingers are completely bent [42, 43].
Acro-osteolysis and calcinosis of tissues in systemic sclerosis
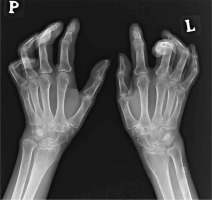
Osteolysis of the distal phalanges of fingers is a serious complication in SSc, and its incidence ranges from 20 to 40%. It occurs more often in the distal phalanges of the fingers, but may also affect the toes. Pathogenesis of the changes includes vascular changes, hypoxia and ischaemia of the distal phalanges, which cause bone resorption and shortening of the distal phalanges. The occurrence of acro-osteolysis in SSc is associated with serious vascular complications, such as fingertip ulcers, pulmonary arterial hypertension, and tissue calcinosis (Fig. 2).
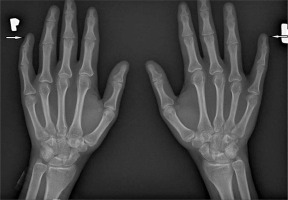
Furthermore, vitamin D deficiency and secondary hyperparathyroidism may be associated with the development of acro-osteolysis. In severe cases, osteomyelitis occurs due to infections of fingertip ulcers [11, 43]. Sakata et al. [44] analysed 124 patients with SSc, finding radiological changes in the hand, such as acro-osteolysis, finger contractures, erosions, narrowing of joint spaces and subluxations in joints in 110 patients. Radiological changes in the bones correlated with the degree of involvement of internal organs and the serological profile of the disease. Acro-osteolysis was found to correlate with interstitial lung disease, calcinosis with pulmonary arterial hypertension and gastrointestinal tract involvement, and the presence of finger contractures with gastrointestinal involvement. Moreover, acro-osteolysis was found more often in patients with SSc with anti-topoisomerase I antibodies (anti-Scl-70 antibodies) [44] (Fig. 3).
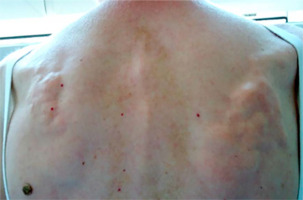
In another study conducted among 42 patients with SSc, acro-osteolysis was confirmed in 58.2% of subjects. The observed changes correlated with the degree of skin involvement assessed on the Rodnan scale [45]. Another complication observed in SSc, which mainly affects the hands, is soft tissue calcinosis. It occurs in approximately 20–40% of patients with SSc, especially in the limited subtype of the disease with the presence of anti-centromere antibodies. The lesions are most often located around the thumb and index finger, but they can affect any other location on the body, with the most painful areas being around the knees and elbows. Soft tissue calcinosis can range in consistency from soft to stone-hard lesions. It has been reported that the occurrence of calcinosis correlates with the presence of acro-osteolysis, telangiectasia, fingertip ulcers, and microangiopathic changes during capillaroscopy of the nail fold vessels [11, 46].
Muscle involvement in systemic sclerosis
In addition to joint and bone complications, muscle involvement may occur in SSc. The incidence of myopathy in SSc ranges from 5 to 96% [47]. The most common symptoms include muscle weakness and muscle pain, occurring in 18–86% of cases; myositis is observed in approximately 10% of patients. According to the EUSTAR study, the incidence of myopathy in the diffuse form of the disease is 37%, and in the limited form 23% [21]. The degree of muscle involvement has been shown to be related to the serological profile of patients with SSc. Inflammatory myopathies occur more often in SSc patients with anti-topoisomerase I antibodies [47]. Other antibodies that correlate with muscle involvement are anti-Ku, anti-U3 RNP, anti-PM/Scl and the newly discovered anti-RuvBL1/2. It has also been found that patients with anti-PM/Scl are more likely to have inflammatory changes in muscle biopsy, and the presence of anti-RNA polymerase III antibodies may be a risk factor for the development of myositis. Polymyositis in patients with SSc occurs in approximately 8–10% of patients. Patients with SSc/polymyositis syndrome are more likely to develop pulmonary fibrosis and heart disease, compared to the group of patients without myositis [48].
Management of musculoskeletal involvement in systemic sclerosis
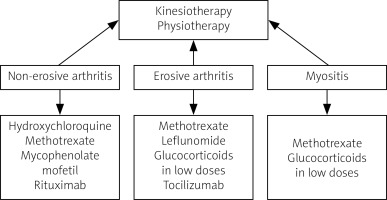
Management of musculoskeletal involvement in SSc includes both non-pharmacological and pharmacological measures. Non-pharmacological treatment should be focused on kinesiotherapy to improve the mobility of patients, and exercises to increase hand mobility are recommended. To date, no fully accepted recommendations for the treatment of arthritis and myositis in SSc have been established. Pharmacotherapy includes disease-modifying drugs, immunosuppressive drugs and biological drugs. Most experts believe that therapy should differ between non-erosive and erosive arthritis. For non-destructive lesions, the drugs of choice are hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate (MTX), mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and rituximab (RTX). In cases of severe destructive arthritis, MTX, leflunomide, low-dose glucocorticosteroids (GCs), and tocilizumab (TCZ) are recommended [49]. In myositis, treatment with MTX and GCs provides improvement, although therapy with GCs, especially at a dose > 15 mg/day calculated as prednisone, is not recommended as it may increase the risk of developing scleroderma renal crisis. No significant response was obtained in studies with cyclophosphamide therapy, although an improvement in muscle involvement was observed after treatment with MMF. There are clinical trials and case reports of treatment of myositis in SSc with biological drugs (TCZ, RTX) in which clinical improvement was achieved. Uncontrolled trials in small groups of patients with SSc/myositis syndrome treated with intravenous infusions of immunoglobulins show promising results [50–52].
An overview of management in SSc with musculoskeletal symptoms is presented in Figure 4.
Conclusions
Involvement of the musculoskeletal system is one of the most common manifestations of SSc. Symptoms may be diverse, ranging from pain or inflammation of joints, changes in tendons and tendon sheaths, to involvement of soft tissues, calcinosis, resorption of distal phalanges, or muscle involvement. Changes in the musculoskeletal system, especially in the hands, often lead to deterioration of the quality of life and disability of patients, and may even cause increased mortality. Moreover, musculoskeletal involvement often indicates a more severe course of the disease, with the presence of serious vascular and organ complications. A more detailed understanding of the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of changes in the musculoskeletal system may be helpful in introducing new therapeutic options for patients with SSc.